A painful shoulder can make even simple tasks difficult to do. You might find it hard to use your arm or your hand when you have pain. But getting the right treatment can help. Shoulder pain is any pain in or around your shoulder joint. You may feel the pain most when you reach behind your back or overhead. There are many reasons why you may get a painful shoulder.
Opening Hours : Monday to Saturday - 8am to 10pm
-
karnav1985@yahoo.com -
Call Now
+ (91) - 92657 01776
Shoulder Surgery
SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY SURGERY
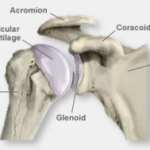
The two main bones of the shoulder are the humerus and the scapula (shoulder blade).The joint cavity is cushioned by articular cartilage covering the head of the humerus and face of the glenoid. The scapula extends up and around the shoulder joint at the rear to form a roof called the acromion, and around the shoulder joint at the front to form the coracoid process.
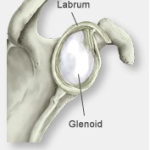
The end of the scapula, called the glenoid, meets the head of the humerus to form a glenohumeral cavity that acts as a flexible ball-and-socket joint. The joint is stabilized by a ring of fibrous cartilage surrounding the glenoid called the labrum.
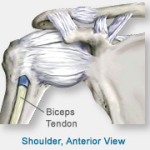
Ligaments connect the bones of the shoulder, and tendons join the bones to surrounding muscles. The biceps tendon attaches the biceps muscle to the shoulder and helps to stabilize the joint.
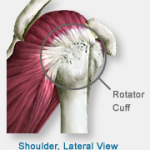
Four short muscles originate on the scapula and pass around the shoulder where their tendons fuse together to form the rotator cuff.All of these components of your shoulder, along with the muscles of your upper body, work together to manage the stress your shoulder.
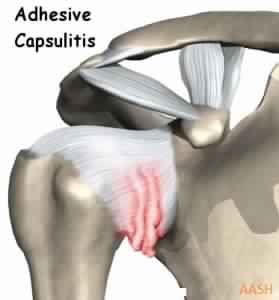
Frozen Shoulder is an extremely painful condition in which the shoulder is completely or partially unmovable (stiff). It is one of the most painful conditions of the shoulder.
Three stages of development:
Typical Primary frozen shoulder develops slowly, and in three phases:
Freezing phase: Pain increases with movement and is often worse at night. There is a progressive loss of motion with increasing pain. This stage lasts approximately 2 to 9 months.
Frozen phase: Pain begins to diminish, however, the range of motion is now much more limited, as much as 50 percent less than in the other arm. This stage may last 4 to 12 months.
Thawing phase: The condition may begin to resolve. Most patients experience a gradual restoration of motion over the next 12 to 42 months.
Treatment:
If nothing is done most frozen shoulders improve significantly over 2-4 years after onset. However the pain and limitations of the stiff shoulder generally require treatment. The treatment required depends on the severity of the pain and stiffness. These include:
Physiotherapy – to prevent any further stiffness and regain range of motion
Painkillers and anti-inflammatories
Surgery – Surgery has been shown to be of benefit in both the early and later stages of a Frozen Shoulder. This may involve an arthroscopic Capsular release or Manipulation Under Anaesthetic (MUA). We prefer the Capsular release procedure. It is excellent for both pain relief and restoring movement, with a success rate of 96% at 6 months. Intensive physiotherapy is essential after the surgery.
WHAT IS IT?
The rotator cuff is a group of tendons that connects the four muscles of the upper shoulder to the bones the strength of the cuff allows the muscles to lift and rotate the humerus (the bone of the upper arm).
A tear may result suddenly from a single traumatic event or develop gradually. When the tendons or muscles of the rotator cuff tear, the patient is no longer able to lift or rotate his or her arm with the same range of motion as before the injury
CAUSES:
Injury, especially while trying to lift or catch a heavy object
Overuse, especially after a period of inactivity
Poor blood supply to an area of the cuff (which occurs with increasing age)
A fall on an outstretched hand
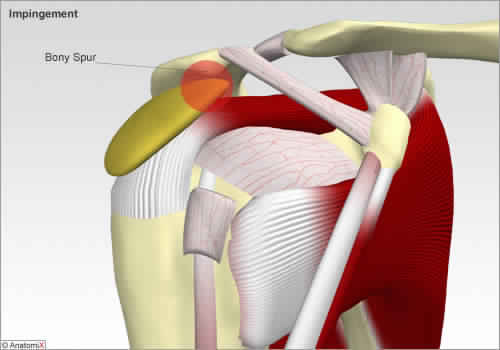
A gradual weakening of the tendons of the shoulder, often associated with impingement
PREVENTION:
Avoid excessive overhead activities.
Strengthen your shoulders and do not try to play or work through the pain.
TREATMENT:
Painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications
Physiotherapy – keeps your shoulder strong and flexible and reduce the pain and weakness
Surgery is required –
If the tear follows an injury
When pain and weakness is not improved with medicine and physiotherapy
- The goal of any surgery is to relieve the pain and improve the shoulder strength. This requires a long period of physiotherapy in addition to the surgery.
- Surgery may be done (keyhole) Arthroscopy or Open, or a combination of the two, know as a Mini-repair.
- Some tears are too large to repair and are known as 'Massive cuff tear'.
What is Glenoid Labrum Tear ?
The shoulder joint has three bones: the shoulder blade (scapula), the collarbone (clavicle), and the upper arm bone (humerus). The head of the upper arm bone (humeral head) rests in a shallow socket in the shoulder blade called the glenoid. The head of the upper arm bone is usually much larger than the socket, and a soft fibrous tissue rim called the labrum surrounds the socket to help stabilize the joint. The rim deepens the socket by up to 50% so that the head of the upper arm bone fits better. In addition, it serves as an attachment site for several ligaments.
Symptoms of Glenoid Labrum Tear
The symptoms of a tear in the shoulder socket rim are very similar to those of other shoulder injuries. Symptoms include:
- Pain, usually with overhead activities
- Catching, locking, popping, or grinding
- Occasional night pain or pain with daily activities
- A sense of instability in the shoulder
- Decreased range of motion
- Loss of strength
Diagnosis of Glenoid Labrum Tear
If you are experiencing shoulder pain, your doctor will take a history of your injury. You may be able to remember a specific incident or you may note that the pain gradually increased. The doctor will do several physical tests to check range of motion, stability, and pain. In addition, the doctor will request x-rays to see if there are any other reasons for your problems. Because the rim of the shoulder socket is soft tissue, x-rays will not show damage to it. The doctor may order a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. In both instances, a contrast medium may be injected to help detect tears.
Tears can be located either above (superior) or below (inferior) the middle of the glenoid socket. A SLAP lesion (superior labrum, anterior [front] to posterior [back]) is a tear of the rim above the middle of the socket that may also involve the biceps tendon.A tear of the rim below the middle of the glenoid socket that also involves the inferior glenohumeral ligament is called a Bankart lesion. Tears of the glenoid rim often occur with other shoulder injuries, such as a dislocated shoulder (full or partial dislocation).
Risk Factors/Prevention of Glenoid Labrum Tear
Injuries to the tissue rim surrounding the shoulder socket can occur from acute trauma or repetitive shoulder motion. Examples of traumatic injury include:
- Falling on an outstretched arm
- A direct blow to the shoulder
- A sudden pull, such as when trying to lift a heavy object
- A violent overhead reach, such as when trying to stop a fall or slide
- Throwing athletes or weightlifters can experience glenoid labrum tears as a result of repetitive shoulder motion.
Treatment of Glenoid Labrum Tear
Until the final diagnosis is made, your physician may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication and rest to relieve symptoms. Rehabilitation exercises to strengthen the rotator cuff muscles may also be recommended. If these conservative measures are insufficient, your physician may recommend arthroscopic surgery.
During arthroscopic surgery, the doctor will examine the rim and the biceps tendon. If the injury is confined to the rim itself, without involving the tendon, the shoulder is still stable. The surgeon will remove the torn flap and correct any other associated problems. If the tear extends into the biceps tendon or if the tendon is detached, the shoulder is unstable. The surgeon will need to repair and reattach the tendon using absorbable tacks, or sutures.
Tears below the middle of the socket are also associated with shoulder instability. The surgeon will reattach the ligament and tighten the shoulder socket by folding over and “pleating” the tissues.
What is it?
A dislocated shoulder is an injury in which your upper arm bone pops out of the cup-shaped socket that's part of your shoulder blade. The shoulder is the body's most mobile joint, which makes it susceptible to dislocation.
